Cyber Insurance Costs For Small to Mid-sized Organizations
As cyber threats evolve and make headlines, business owners, IT directors, executives, and finance directors are increasingly faced with a critical question: “How much does cyber insurance cost?”
This article examines cyber insurance costs, revealing the various factors influencing premiums for organizations like yours.
We’ll explore small and midsize businesses and local government offices’ unique challenges, offering insights into how they can balance protection with affordability.
Join us as we navigate the world of cyber insurance premiums, shedding light on this essential yet often overlooked aspect of safeguarding your organization’s digital assets and future.
A quick understanding of cyber insurance
In this section, we’ll explore the importance of cyber insurance for small to midsize businesses and local government offices, discussing primary and secondary coverage options and highlighting common cyber risks and threats.
1. Why Cyber Insurance is Crucial
With cyber threats rising, cyber insurance has become an indispensable tool for organizations of all sizes to secure their digital assets.
Cyber insurance provides financial support and expert assistance in the aftermath of a cyber incident, helping businesses recover and maintain operations. In addition, cyber insurance ensures long-term stability and resilience for businesses and local government offices, which often need more in-house resources and expertise to manage cyber risks.
2. Primary and Secondary Coverage Options
Cyber insurance policies typically offer a range of primary and secondary coverage options to cater to different organizational needs.
Primary coverage options include:
- Data breach response: Covers the costs of notifying affected individuals, providing credit monitoring services, and managing public relations efforts following a data breach.
- Network security liability: Protects against third-party claims arising from cyber incidents, such as data breaches or denial-of-service attacks.
- Business interruption: Provides financial support for lost income and additional expenses incurred due to a cyber event disrupting business operations.
3. Secondary coverage options may include:
- Cyber extortion: Covers the costs of responding to ransomware attacks or other extortion attempts.
- Reputational harm: Helps offset the costs of addressing damage to an organization’s reputation following a cyber incident.
- Regulatory fines and penalties: Provide coverage for fines and penalties imposed by regulatory bodies due to non-compliance with data protection regulations.
4. Common Cyber Risks and Threats

SMBs and local government offices face various cyber risks and threats, including:
- Phishing attacks: Cybercriminals often use deceptive emails to trick employees into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware.
- Ransomware: This type of malware encrypts an organization’s data, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid to the attacker.
- Insider threats: Disgruntled or careless employees may intentionally or accidentally compromise an organization’s digital assets.
- Supply chain attacks: Cybercriminals may target an organization’s vendors or service providers to gain access to the organization’s systems and data.
Factors Influencing Cyber Insurance Costs
In this section, we’ll delve into the various factors that influence the cost of cyber insurance for SMBs and local government offices, helping you better understand how premiums are determined.
Business Size and Industry
The size of your organization and its industry are significant factors that impact cyber insurance costs. For example, larger businesses or those in high-risk industries, such as finance or healthcare, may face higher premiums due to the increased potential for data breaches and the value of the sensitive information they handle.
Security Measures and Policies in Place

Insurers consider the effectiveness of an organization’s cybersecurity measures and policies when determining premiums.
Businesses with robust security frameworks, regular employee training, and up-to-date software will likely receive more favorable rates as they demonstrate a lower risk of cyber incidents.
Past Claims and Incident History
An organization’s cyber claims and incidents history can influence its insurance costs. For example, a track record of frequent claims or unresolved security issues may lead to higher premiums, indicating a higher likelihood of future incidents.
Coverage Limits and Deductibles
The extent of coverage you choose will directly impact your cyber insurance costs. For example, higher coverage limits and lower deductibles result in higher premiums, while lower limits and higher deductibles can reduce the overall cost.
It’s essential to balance comprehensive protection and affordability when selecting coverage options.
Geographic Location and Regulatory Landscape
The geographic location of your business and the prevailing regulatory landscape can also affect cyber insurance costs.
Pricing Cyber Insurance: A Breakdown
 This section will provide a detailed breakdown of cyber insurance pricing, including average premium costs, local government considerations, and potential discounts or hidden fees.
This section will provide a detailed breakdown of cyber insurance pricing, including average premium costs, local government considerations, and potential discounts or hidden fees.
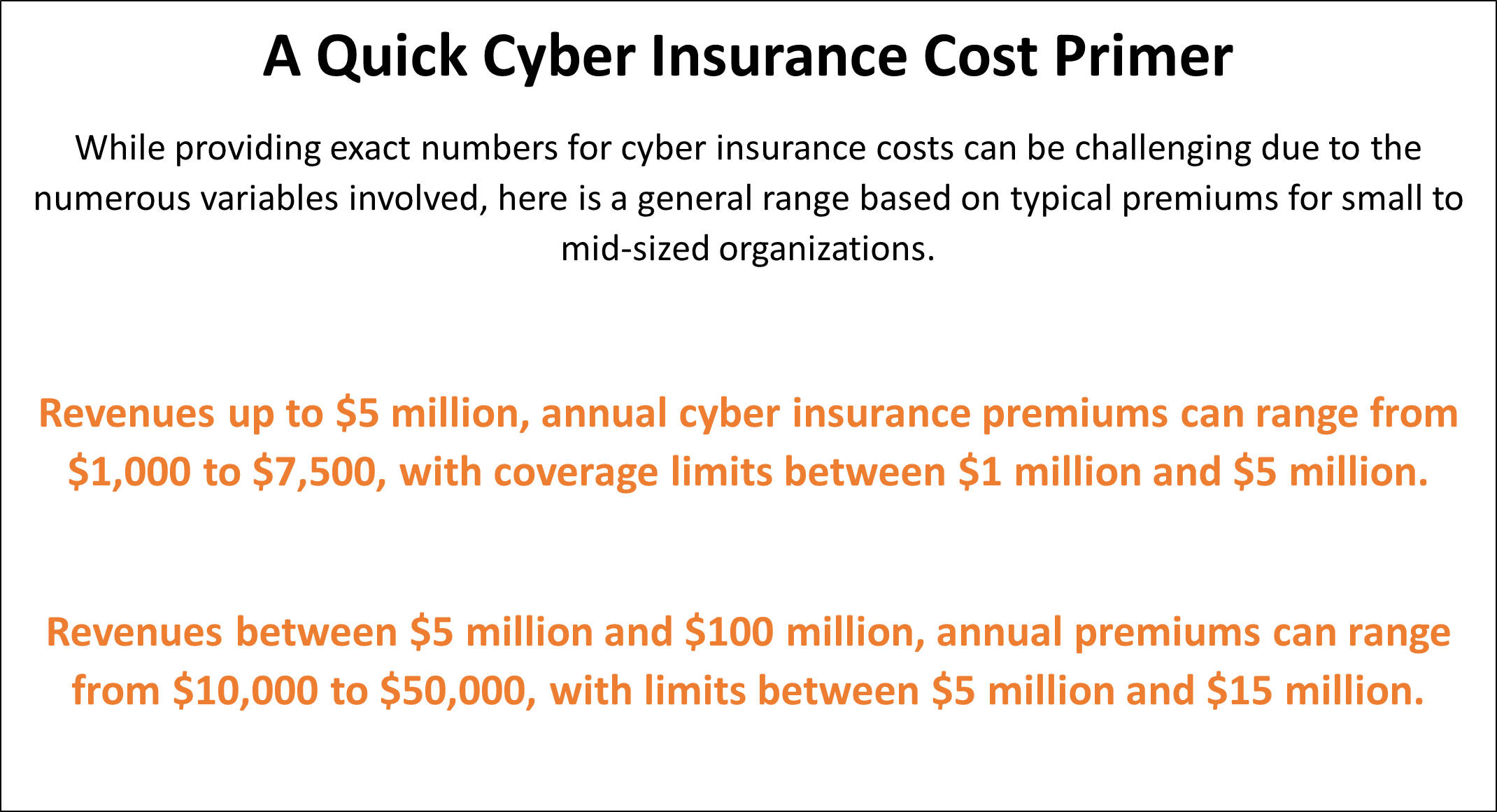
1. Average Premium Costs for Small to Mid-Sized Businesses
The average premium cost for cyber insurance varies depending on several factors, including the size of your business, industry, and specific coverage needs.
Generally, SMBs can expect annual premiums to range between $1,000 and $7,500 for $1 million in coverage, though costs can be higher for businesses in high-risk industries or with extensive coverage requirements.
2. Local Government Office Premiums
Local government offices must consider additional factors when assessing cyber insurance premiums. For example, these organizations often handle sensitive public data, making them targets for cybercriminals.
Due to their unique risk profiles and the potential for higher legal liabilities, local government offices may face higher premiums than private sector SMBs.
3. Policy Bundles and Discounts
Many insurance providers offer policy bundles and discounts to help businesses save on cyber insurance costs. Bundling cyber insurance with other policies, such as general liability or property insurance, can lead to significant savings.
Additionally, insurers may provide discounts to organizations that demonstrate strong cybersecurity practices or participate in risk management programs.
4. Unforeseen Costs and Hidden Fees
When evaluating cyber insurance policies, consider potential unforeseen costs and hidden fees. For example, some policies may include additional charges for policy endorsements, risk assessments, or claims assistance services. Make sure to carefully review the policy terms and ask your insurance agent about any additional costs or fees that may apply.
Understanding the components contributing to cyber insurance pricing can help SMBs and local government offices make informed decisions when selecting coverage. In addition, by taking the time to research and compare policies, you’ll be better equipped to find the right protection at a price that fits your budget.
Balancing Protection and Affordability
 Achieving the right balance between robust cyber insurance coverage and affordability is crucial. In this section, we’ll explore strategies to tailor your cyber insurance policy while keeping costs in check.
Achieving the right balance between robust cyber insurance coverage and affordability is crucial. In this section, we’ll explore strategies to tailor your cyber insurance policy while keeping costs in check.
Assessing Your Organization’s Risk Profile
Begin by conducting a thorough risk assessment to identify your organization’s unique vulnerabilities and exposures.
Evaluating cyber threats and their potential impact on your operations will help you determine the appropriate level of insurance coverage.
Customizing Coverage to Match Unique Needs
Not all cyber insurance policies are created equal. Customize your coverage to match your organization’s specific needs and risk profile.
This may involve selecting higher limits for certain exposures or opting for endorsements that address unique risks, such as social engineering attacks or ransomware incidents.
Investing in Cybersecurity Measures to Lower Premiums
Implementing strong cybersecurity measures can help lower your insurance premiums. For example, insurers often provide discounts to organizations that demonstrate a commitment to risk mitigation, such as maintaining up-to-date security software, providing employee training, and conducting regular security audits.
Investing in cybersecurity lowers your premiums and strengthens your organization’s defenses against cyber threats.
Regularly Reviewing and Updating Your Policy
As your organization evolves, so should your cyber insurance policy. Therefore, regularly review and update your coverage to align with your risk profile and operational needs.
This may involve adjusting coverage limits, adding new endorsements, or reevaluating your deductible. Staying proactive in managing your policy will help you maintain adequate protection at the best possible price.
Selecting the Right Cyber Insurance Provider
 Choosing the ideal cyber insurance provider involves careful consideration of several factors. This section will guide you through the key evaluation aspects when selecting an insurance provider that meets your organization’s unique needs.
Choosing the ideal cyber insurance provider involves careful consideration of several factors. This section will guide you through the key evaluation aspects when selecting an insurance provider that meets your organization’s unique needs.
1. Comparing Coverage Offerings and Pricing
First and foremost, compare different providers’ coverage offerings and pricing structures.
Look for policies that address your organization’s specific risks and vulnerabilities while offering competitive pricing. Then, examine each policy’s exclusions, limitations, and deductibles to ensure you get the best investment value.
2. Evaluating Provider Expertise and Customer Support
A knowledgeable provider should be able to guide you through the complexities of cyber insurance, helping you select appropriate coverage levels and endorsements.
Additionally, consider the quality of their customer support, as responsive and attentive service is invaluable during the claims process.
3. Verifying Financial Stability and Industry Reputation
Research the financial stability and industry reputation of potential providers. A financially secure provider ensures they have the resources to pay claims promptly, while a strong reputation signifies trustworthiness and reliability.
Check independent ratings from organizations like A.M. Best, Standard & Poor’s, and Moody’s to assess the financial health of prospective insurers.
4. Seeking Recommendations and Testimonials from Peers
Finally, gather recommendations and testimonials from your industry peers. This firsthand feedback can offer valuable insights into the experiences of others in similar organizations, helping you make a more informed decision.
Ask colleagues, industry associations, or online forums for their opinions on specific providers and their experiences with cyber insurance claims.
How To Keep Cyber Insurance Costs Down
Navigating the world of cyber insurance can be daunting, but it’s essential to balance robust protection and affordability. Here are some actionable tips to help keep your cyber insurance costs down without compromising your organization’s security:
Strengthen your cybersecurity measures.
 Implementing robust cybersecurity measures can significantly reduce your risk profile, leading to lower insurance premiums. Some steps to consider include:
Implementing robust cybersecurity measures can significantly reduce your risk profile, leading to lower insurance premiums. Some steps to consider include:
- Adopting multi-factor authentication
- Regularly updating software and hardware
- Providing ongoing employee cybersecurity training
- Developing a comprehensive incident response plan
Customize your policy
Work with your insurance provider to tailor your coverage based on your organization’s unique risk profile. Avoid purchasing unnecessary coverage that may inflate your premiums. Instead, focus on the coverage that addresses the most critical threats to your organization.
Shop around for the best deal.
Take the time to research multiple insurance providers and compare their offerings, pricing, and reputation. This will allow you to find the best policy for your organization at the most competitive price.
Consider higher deductibles
Opting for a higher deductible can lead to lower premiums. However, make sure to weigh the potential savings against the financial impact of a cyber incident. Choose a deductible your organization can comfortably manage in case of a claim.
Regularly review and update your policy.
Your insurance needs may change as your organization evolves and the cybersecurity landscape shifts. Regularly reviewing and updating your policy will ensure you maintain the right level of coverage without paying for unnecessary protection.
Conclusion
This brief article explored the factors influencing cyber insurance costs, including business size, industry, security measures, past claims, coverage limits, and more.
We’ve delved into the intricacies of pricing and how to balance protection with affordability.
Finally, we’ve discussed the importance of selecting the right cyber insurance provider to meet your organization’s unique needs.
As we move forward in this increasingly digital world, staying up-to-date with the latest technologies is essential for remaining cyber-secure. As a small to midsized organization or local government office, you protect your organization and its stakeholders from ever-evolving cyber-attack threats.
Cyber insurance can be an asset in your cybersecurity strategy, providing the financial support needed to recover from potential incidents.
You’re making a crucial investment in your organization’s future by taking the necessary steps to evaluate and choose the right insurance provider.
Interested in Digging Deeper
If you want to dig deeper into cyber insurance for your organization, check out The Ultimate Guide to Cyber Insurance. It will help you get a comprehensive look into your options and help you choose the right coverage.





