Steps to protect your e-signature from digital signature fraud
As our world becomes increasingly digital, secure and trustworthy electronic transactions are more important than ever. And digital signature fraud is becoming more and more prevelant.
Digital signatures have become vital in ensuring the authenticity and integrity of online agreements, contracts, and other documents. However, with the rise in digital signature usage comes the growing threat of digital signature fraud.
In this quick guide, we’ll explore how cybercriminals exploit e-signatures, the various forms of digital signature fraud, and the steps you can take to protect yourself and your business.
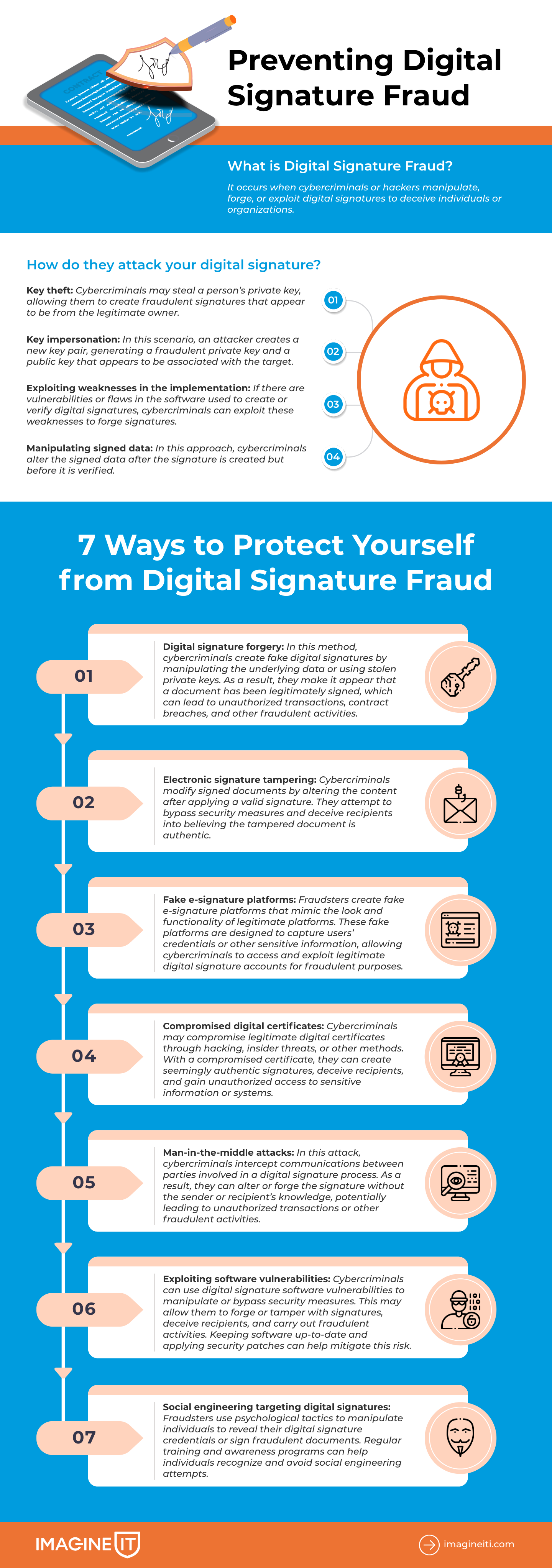
What is Digital Signature Fraud?
Digital signature fraud occurs when cybercriminals or hackers manipulate, forge, or exploit digital signatures to deceive individuals or organisations. This type of fraud often raises the question: Can a digital signature be misused? The answer is, unfortunately, yes. Such misuse of digital signature methods can lead to financial loss, reputational damage, and legal issues.
To effectively combat digital signature fraud, it’s essential to understand the various techniques employed by cybercriminals and the weaknesses they exploit.
Why Digital Signature Fraud Matters ?
Digital signature fraud poses a significant threat to small and mid-sized organisations and can severely impact reputation, financial stability, and competitive position. As a growing form of digital fraud, this type of attack often overlaps with broader electronic signature fraud incidents.
By understanding the risks and implementing robust security measures, SMBs can mitigate the impact of digital signature fraud and maintain trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
Exactly how do they attack your digital signature
Digital signature fraud occurs when cybercriminals manipulate or forge digital signatures to deceive others into believing a document or communication is legitimate. Digital signatures use public key cryptography to ensure the authenticity and integrity.
The process involves a private key for signing and a public key for verification. Here’s a breakdown of how cybercriminals misuse digital signature methods:
Key Theft
Cybercriminals may steal a person’s private key, allowing them to create fraudulent signatures that appear to be from the legitimate owner. This can be accomplished through phishing attacks, malware, or compromising a person’s device.
Key Impersonation
In this scenario, an attacker creates a new key pair, generating a fraudulent private key and a public key that appears to be associated with the target. The attacker then signs the document using the fraudulent private key. To make the impersonation convincing, the attacker can manipulate metadata or create fake credentials to support the forged public key.
Exploiting Weaknesses in the Implementation
If there are vulnerabilities or flaws in the software used to create or verify digital signatures, cybercriminals can exploit these weaknesses to forge signatures. For example, they may manipulate the signature algorithm or tamper with the signed document’s hash value to bypass verification checks.
Manipulating Signed Data
In this approach, cybercriminals alter the signed data after the signature is created but before it is verified. This could involve changing the contents of a signed document or modifying the data used to generate the signature’s hash value. The goal is to create a scenario in which the tampered data still appears to be valid when the digital signature is verified.

Early Detection is Key
It’s not easy to pick a fraud suspect out of a crowd, but certain behavioural red flags can help. Early detection is critical to:
- Minimise financial and reputational damage
- Preserve legal standing
- Prevent further exploitation
- Enhance security measures
- Boost company confidence
Implementing early detection requires technical controls, strong policies, and employee awareness.
Digital signature forgery
Cybercriminals create fake digital signatures by manipulating the underlying data or using stolen private keys. This is one of the most common forms of digital signature fraud, leading to unauthorized transactions and fraudulent activities. Detecting such forgery can be challenging because the signature may appear legitimate.
Electronic signature tampering
Cybercriminals alter a signed document’s content after applying a legitimate signature. This form of electronic signature fraud often results in disputes, financial losses, and legal issues.
Fake e-signature platforms
Fraudsters build fake platforms to capture user credentials or sensitive information, which are then used the misuse of digital signature accounts.

Compromised digital certificates
When a certificate is compromised, attackers can create signatures that appear valid. This type of digital signature fraud can be difficult to detect without specialized tools.
Man-in-the-middle attacks
Cybercriminals intercept and alter communications between parties involved in the signing process, enabling unauthorised changes or fraudulent approvals.
Exploiting software vulnerabilities
Security gaps in digital signing software allow attackers to bypass protections and manipulate signatures. Frequent updates and patches are essential to reduce this risk.
Social engineering targeting digital signatures
Fraudsters employ psychological manipulation to deceive individuals into signing fraudulent documents or disclosing sensitive information. By targeting the digital signature aspect of a transaction, they can gain unauthorized access to sensitive information and carry out other forms of digital signature fraud. Regular training helps employees recognise such attempts.
Cybersecurity and Authentication Vulnerabilities in Digital Signatures
- Weak authentication opens doors for digital signature fraud.
Common vulnerabilities include:
- Weak password policies
- Insecure key storage
- Phishing susceptibility
Digital Certificate Fraud and Fraudulent Document Signing
Digital certificates are a crucial component of digital signatures, as they authenticate the signer’s identity and validate the signed document’s integrity. However, cybercriminals can create fraudulent digital certificates or compromise legitimate ones, allowing them to sign documents with seemingly valid certificates.
This advanced form of digital fraud often requires expert analysis to uncover.
Security Breaches and Legal Implications of Digital Signature Fraud
Digital signature fraud can result in serious legal implications, as forged or tampered signatures can lead to unauthorized transactions, breaches of contracts, and other violations of law.
Businesses and individuals can also face significant financial losses and reputational damage because of digital signature fraud. Furthermore, security breaches resulting from digital signature fraud can expose sensitive information, leaving organizations vulnerable to further attacks or legal ramifications.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning advancements have opened up new possibilities for detecting and preventing digital signature fraud. By analyzing large datasets and identifying patterns of fraudulent behavior, AI-driven systems can flag potential instances of fraud and help organizations respond more quickly to threats.
AI and machine learning can significantly enhance fraud detection through:
- Anomaly Detection: AI-powered systems can analyze digital signature usage patterns to identify unusual or potentially fraudulent activity, such as multiple signatures originating from the same IP address in a short period.
- Forgery Detection: Machine learning algorithms can be trained to recognize subtle differences between genuine and forged digital signatures, making it easier to spot attempts at signature forgery.
- Real-Time Monitoring: AI-driven solutions can monitor digital signature processes in real time, providing organizations with early warning of potential security breaches or instances of fraud.
By incorporating AI-driven tools and techniques into their digital signature security strategies, organizations can stay one step ahead of cybercriminals and better protect themselves from the risks associated with digital signature fraud.
7 Ways to Protect Yourself from Digital Signature Fraud
To protect yourself and your organization, consider implementing the following best practices:
1. Implement Strong Authentication Measures
Use multi-factor authentication, strong passwords, and secure key storage to minimize the risk of authentication vulnerabilities.
2. Keep Software and Systems Up to Date
Regularly update your digital signature software and other systems to eliminate vulnerabilities that can enable the misuse of digital signature assets.
3. Validate Digital Certificates
Always verify the authenticity and validity of digital certificates before accepting digitally signed documents. Make use of certificate revocation lists (CRLs) and trusted certificate authorities (CAs) to ensure the legitimacy of certificates.
4. Encrypt Sensitive Data
Protect sensitive information by encrypting it when it’s stored and transmitted. This adds an extra layer of security, making it more difficult for cybercriminals to access the data.
5. Perform Regular Audits
Conduct regular audits of your digital signature processes and security measures to identify potential vulnerabilities and areas for improvement.
6. Train Employees on Phishing Prevention
Phishing attacks are common methods cybercriminals use to gain access to sensitive information or authentication credentials. Ensure that employees are trained to reduce the chance of digital fraud infiltration.
7. Establish Clear Policies and Procedures
Develop and enforce clear policies and procedures for handling digital signatures, including document signing and approval processes. Make sure employees understand their roles and responsibilities within these processes.
The crucial role of your Managed IT Provider
Your IT provider plays a crucial role in preventing digital signature fraud by implementing robust security measures and maintaining up-to-date systems. They are responsible for setting up multi-factor authentication, configuring access control policies, and ensuring the digital signature software used by your organisation is secure and free from vulnerabilities.
Additionally, they must monitor your network for potential threats and provide regular employee training on cybersecurity best practices, specifically focusing on digital signature fraud prevention.
To protect yourself from digital signature fraud, it’s essential to have a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that includes strong encryption, intrusion detection, regular security audits, and a proactive incident response plan.
Partnering with knowledgeable cybersecurity solution providers is the key to safeguarding your organisation’s sensitive information and digital signature processes.

Final Thoughts
The increasing reliance on digital signatures for electronic transactions highlights the need for robust security measures to prevent digital signature fraud. Organisations can minimise risk and maintain the trust and integrity of their digital transactions by understanding the various forms of fraud, implementing best practices, and leveraging emerging technologies like AI.
At Imagine IT, we help organisations strengthen their defences through our cybersecurity solutions in Sterling, Zeeland, Bloomington, Wichita, or Garden City.
Reach Out to Imagine IT for Expert Guidance
Minnesota: Bloomington – 952.224.2900
Michigan: Grand Rapids – 616.773.2700
Kansas: Sterling, Garden City, Wichita – 620.278.3600
Digital Signature Fraud: FAQs
What is digital signature fraud?
Digital signature fraud occurs when cybercriminals manipulate, forge, or exploit digital signatures to deceive individuals or organizations. This type of fraud can have serious consequences, including financial loss, reputational damage, and legal issues.
How do cybercriminals forge digital signatures?
Cybercriminals can forge digital signatures by replicating a legitimate user’s signature, creating a fake one, or tampering with an existing signature to alter its meaning or appearance.
What are the legal implications of digital signature fraud?
Legal implications of digital signature fraud can include unauthorized transactions, breaches of contracts, and other violations. Businesses and individuals can also face significant financial losses and reputational damage because of digital signature fraud.
How can I protect my organization?
To protect your organization from it, implement strong authentication measures, educate your team about the risks, monitor for suspicious activity, keep software and systems up to date, validate digital certificates, encrypt sensitive data, develop a response plan, perform regular audits, train employees on phishing prevention, and collaborate with industry peers.
What role do digital certificates play?
Digital certificates are a crucial component of digital signatures, as they authenticate the signer’s identity and validate the signed document’s integrity. Unfortunately, cybercriminals create fraudulent digital certificates or compromise legitimate ones, allowing them to sign documents with seemingly valid certificates.