In the current digital era, cybersecurity is more important than ever. Brute force attacks are one of the most popular ways to hack. Hackers use a brute force attack to try out every conceivable character combination in search of the right password.
Brute force attacks are simple to execute manually or automatically, allowing even novice hackers to try them. Once the password is discovered, hackers can access a system or account without authorization, making your confidential data and information vulnerable.
By adhering to preventative procedures, you can safeguard yourself from any potential harm produced by brute force attacks. Keep reading to discover everything you need to know about brute force attacks and how to defend yourself against them.
What is a Brute Force Attack?
Hackers employ brute force assaults to gain unauthorized access to user accounts, company networks, and systems. Cracking passwords, login credentials, and encryption keys require trial and error.
It is a simple but successful technique where the hacker uses a computer to try numerous username and password combinations to narrow down the possibilities until they find the right login credentials.
What are Some Examples of a Brute Force Attack?
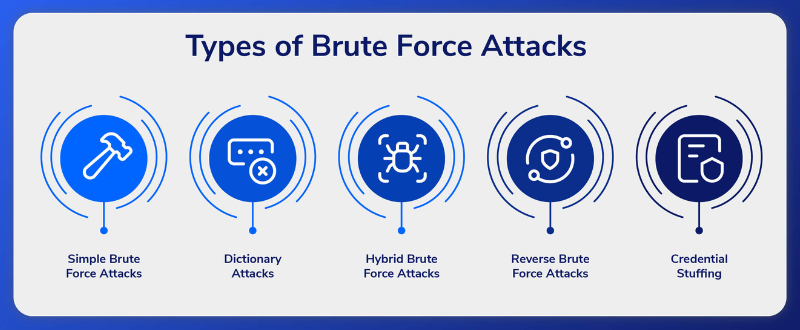
Hackers can use different brute force techniques to obtain unauthorized access and steal personal data.
Attack Using Simple Brute Force
The first kind is a straightforward brute force attack, which is manually guessing a user’s login information without the aid of any program. Personal identification numbers (PINs) or common password combinations are typically used in this assault.
Many people still reuse the same password across many websites and use weak passwords like “password123” or “1234,” which is the cause. Additionally, hackers might try to guess passwords by learning the person’s favorite sports team.
Dictionary Attack
A dictionary attack is the second sort of attack, in which the attacker chooses a target and compares potential passwords to their username. Although this technique technically isn’t a brute force attack, it can be crucial to a hacker’s password-cracking strategy.
Attack Using Hybrid Brute Force
A dictionary assault and a straightforward brute force attack are combined to create the third kind of brute force attack. Using a known username as a starting point, hackers launch this assault before using a combination of dictionary and straightforward brute force techniques to discover the account’s correct login details.
Attack Using Reverse Brute Force
An attacker employs a known password, typically learned through a network breach. Using lists of millions of usernames, the attacker utilizes that password to look for a matching login credential. Additionally, they might scan a database of usernames for a probable match using a weak password that is widely used, like “Password123,”
Credential Stuffing
Credential stuffing, which takes advantage of users’ poor password etiquette, is the fifth form of brute force assault. Hackers gather stolen usernames and password pairs and test them on different websites to see if they can access more user accounts.
This technique can be effective if people use the same password and username combination or reuse passwords across numerous accounts and social media profiles.
What is the Motive Behind Brute Force Attacks

For various reasons, hackers utilize brute force attacks to obtain illegal access to other people’s systems or websites. Some typical justifications for conducting a brute force attack, notwithstanding the fact that they may be secretive or irrational, include:
Financial Gains
For financial gain, most hackers break into websites or computer systems. Placing spam adverts on websites allows them to make money through advertising commissions; every time these ads are clicked, the hacker is paid. In addition, hackers might profit financially by selling the activity data of their victims.
Theft of Personal Data
Hackers can fake a person’s identity and get access to their personal accounts, including their financial and medical details, by using brute force attacks. They can launch more extensive attacks by further exploiting this information.
Malware Expansion
Hackers can carry out brute force assaults by infecting the target’s system with malware. It gives them access to other related systems and networks, enabling them to conduct a more thorough attack.
Showcase of Skills
Hackers sometimes use brute force attacks to fool around or show off their hacking abilities without personal animosity.
Damage to a Company’s Reputation
Hackers may also use brute force attacks to change or steal sensitive data from businesses to harm their reputations. They are free to act in a way inconsistent with the company’s essential principles.
Brute Force Attack Tools
It may take some time to guess a user’s email or social media website password, especially if the accounts have strong passwords. To make the procedure easier, hackers have created software and tools to aid in password cracking.
Tools for brute force attacks include password-cracking programs that can decipher username and password combinations that would be very challenging for an individual to figure out on their own. Below are some brute force attack tools that are commonly used:
- Aircrack-ng – A tool package called Aircrack-ng analyses the security of Wi-Fi networks to spy on users, export data, and attack a company via bogus access points and packet injection.
- John the Ripper – John the Ripper is an open-source password recovery program that works with macOS, Unix, and Windows, database servers, web applications, network traffic, encrypted private keys, and document files.
These programs can quickly decrypt different computer protocols, wireless modems, and encrypted storage devices. They can also quickly find weak password combinations.
Furthermore, a brute force attack may require significant computational power. To address this, hackers have created hardware tools that streamline the process, including integrating a device’s CPU and GPU.
When the computing power of the GPU is added, a system can handle many tasks at once, and hackers can break passwords much more quickly.
How to Prevent Brute Force Attacks?
Organizations can improve cybersecurity to fend off brute-force assaults by implementing a variety of tactics, such as the following:
- Increase Password Complexity – Increasing password complexity makes password decryption take longer. Put in place password management rules, such as a requirement for special characters and a minimum passphrase length.
- Limit unsuccessful login attempts – Secure networks and systems by putting in place rules that lock out users for a certain period of time after repeated failed login attempts.
- Hashtag & Encrypt – A brute-force attack requires considerably more time and computational resources when using 256-bit encryption and password hashes. Password combinations are hashed such that they have different hash values by storing strings in a separate database.
- Using CAPTCHAs – These make networks, systems, and websites accessible to people while preventing brute-force attack tools like John the Ripper.
- Implementing two-factor authentication – This type of multifactor authentication adds a layer of login security by requiring two forms of authentication. For instance, users must sign in to a new Apple device using their Apple ID and a six-digit code displayed on a different device previously designated as a trusted device.
How Can Imagine IT Help in Preventing Brute Force Attacks?
Brute force attacks are harmful to your organization’s data, and you can safeguard your organization from cybersecurity attacks by availing of the managed IT services of Imagine IT. Imagine IT provides cybersecurity solutions to organizations of all sizes and sectors. So, what are you waiting for? Contact the professionals of Imagine IT now, and safeguard your organization.






